Research
Circular Accessible Depth: A Robust Traversability Representation for UGV Navigation
Authors: Shikuan Xie, Ran Song, Yuenan Zhao, Xueqin Huang, Yibin Li and Wei Zhang.
This paper has been submitted to IEEE Transactions on Robotics and is under review now.
Pre-printed version available at arXiv.
Background
Most existing work on autonomous navigation focuses on urban self-driving, where only pre-defined and/or structured objects, such as vehicles and pedestrians, are recognized via 3D detection techniques. Such perception approaches may cause serious accidents due to the lack of a robust traversability prediction in the case that some objects do not present in the training dataset or have irregular shapes that cannot be represented by regular 3D boxes. In particular, this problem becomes more pronounced for unmanned ground vehicles (UGV), which inevitably confront irregular obstacles such as trunks, lamp posts, barriers, and even downward stairs when performing searching, inspection, and delivery tasks in environments significantly different from a typical highway for autonomous driving.
Thus, we propose the Circular Accessible Depth (CAD), a robust traversability representation for an unmanned ground vehicle (UGV) to learn traversability in various scenarios containing irregular obstacles. CAD can uniformly represent different kinds of obstacles for predicting the traversability of the surrounding environment, and it predicts the maximum accessible depth in all circular directions centered at the UGV.
To predict CAD, we propose a neural network, namely CADNet, with an attention-based multi-frame point cloud fusion module, Stability-Attention Module (SAM), to encode the spatial features from point clouds captured by LiDAR.
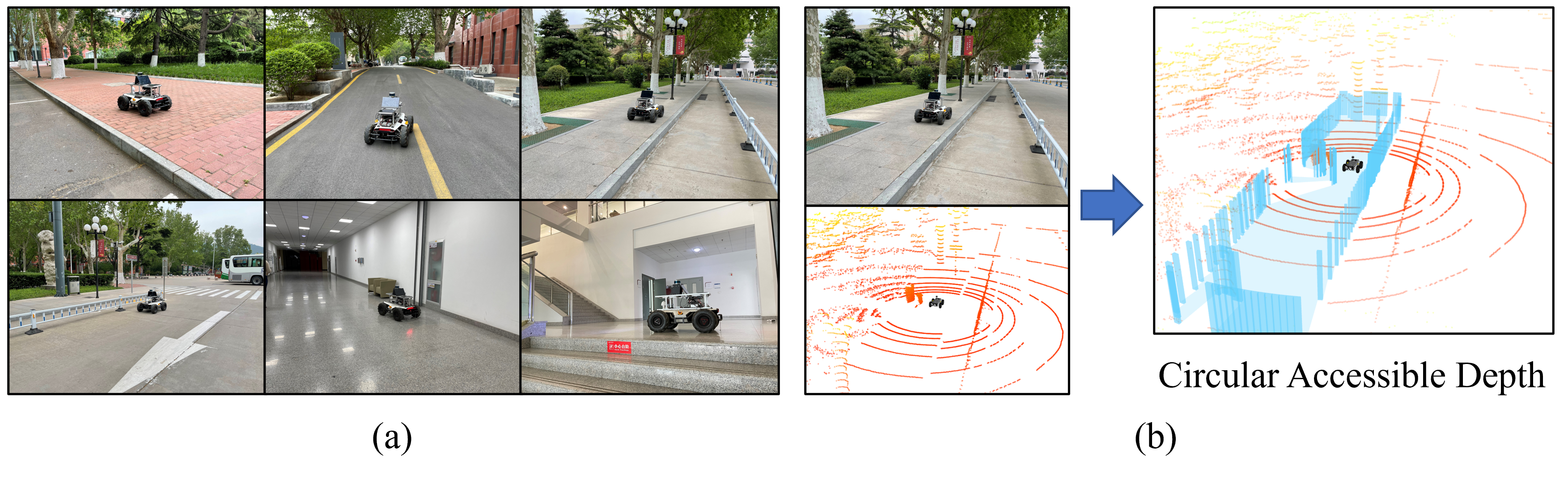
Some typical operating scenarios of UGV and the visualization of CAD are shown below.
Network
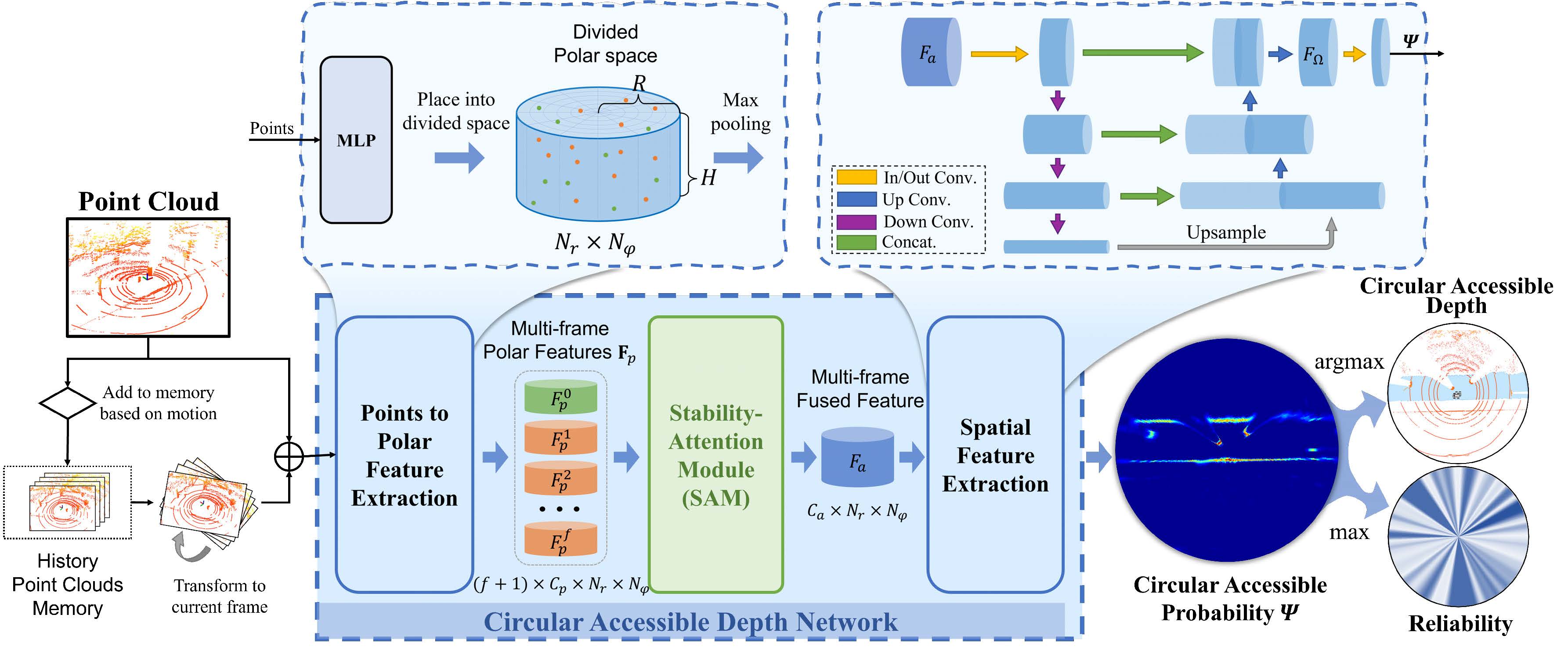
CADNet aims to predict the CAD representation of the surrounding environment by extracting the spatial feature of LiDAR point clouds. The pipeline of the CADNet is shown below, including three main components Points to Polar Feature Extraction, Stability-Attention Module (SAM), and Spatial Feature Extraction.
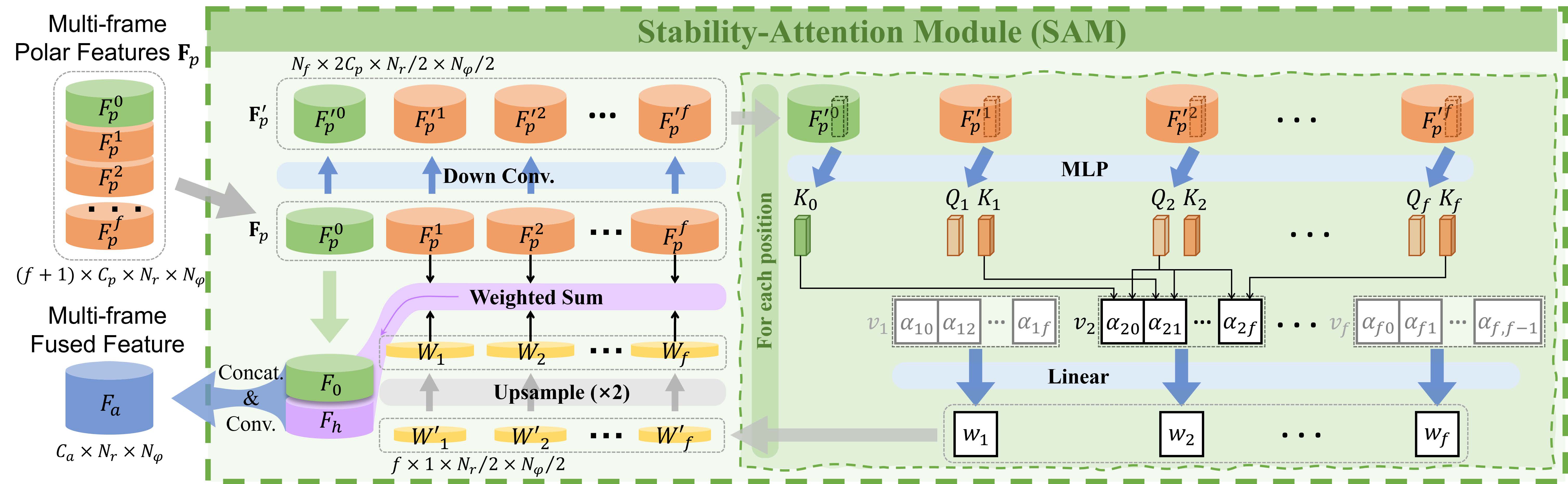
Since single-frame point cloud lacks sufficient information for the prediction of the traversability, multi-frame point clouds fusion is important for traversability prediction. However, the points of dynamic objects will remain while fusing multi frames. Thus, we design an attention-based module, called Stability-Attention Module(SAM) to reduce the interference of historical points of dynamic objects in CAD prediction. The structure of SAM is shown below.
Real-world deployment
We deployed the CAD on a real UGV and tested in real environments, please refer to the youtube video for the real-world performance of our method.
Data collection of CAD
Since most of the existing point cloud annotation tools are oriented to point cloud segmentation and 3D object detection, they are not suitable for our task. I develop a CAD annotation tool with PyQt and OpenGL which applies ArcBall to project 3D space to 2D image. The annotation tool is shown below.
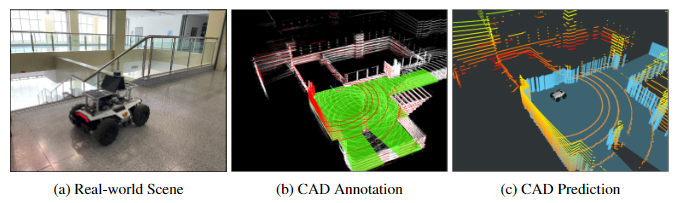
Users can draw CAD ground truth based on the point cloud shown in the annotation tool. This data annotation tool is easy to use and convenient to label some real-world data quickly for training. Thus our method can be implemented in real-world applications easily.
I have open-sourced and maintained the CAD annotation tool CADLabeler in anticipation of a better future for real application of CAD through continuous improvement.

